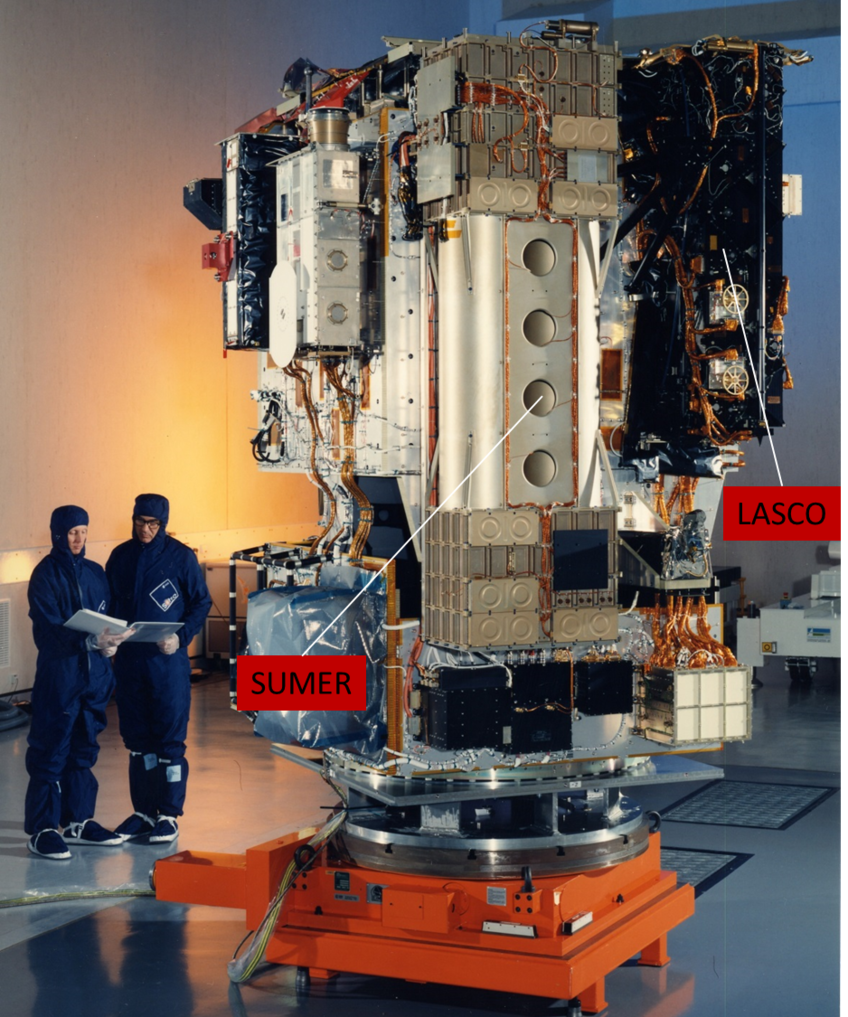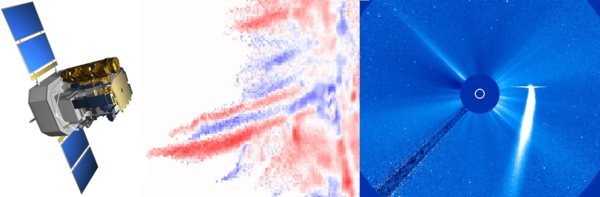
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory – SOHO – carries a suite of instruments to study the Sun from its deep core to the outer corona and the solar wind
SOHO – for almost two decades the workhorse of ESA and NASA for many fields of solar science – is positioned in a halo orbit around the first Lagrangian point. This advantageous vantage allows to observe the Sun uninterrupted and without geocoronal disturbances. The SOHO payload is composed of 12 instruments, three helioseismology instruments (GOLF, VIRGO, MDI), two spectrometers (CDS, SUMER), a disk imager (EIT), two coronagraphs (UVCS, LASCO), three in-situ instruments (CELIAS, COSTEP, ERNE) and a solar wind mapper (SWAN). While some of the instruments have reached the end of their operational lifetime and transited into the data phase, others are fully operational. The LASCO coronagraph has even increased its importance for heliospheric science, since it serves as the third eye for the SECCHI instruments on STEREO. It is foreseen to operate SOHO at least into the early 2020s. So far SOHO has provided an unprecedented breadth and depth of information about the Sun, documented in an impressive, still growing body of scientific and popular literature.

Instruments onboard SOHO
| Instrument | Measurements |
| GOLF: Global Oscillations at low Frequency PI: A. Gabriel; Institute d'Astrophysique Spatiale, France |
Global Sun velocity oscillations |
|
VIRGO: Variability of solar Iradiance and Gravity Oscillations |
Global Sun and low resolution imaging, active cavity radiometers |
| MDI/SOI: Michelson Doppler Imager / Solar Oscillations Investigation PI: P.H. Scherrer;Center for Space Science and Astrophysics, Stanford, USA |
Velocity oscillations, harmonic degree up to 4500 |
| SUMER: Solar Ultraviolet Measurements of Emitted Radiation PI: K. Wilhelm; Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Germany |
Hires normal incidence spectrometer; 50 - 160 nm |
| CDS: Coronal Diagnostic Spectrometer PI: Richard Harrison; Rutherford Appleton Laboratories, UK |
Normal and grazing incidence spectrometers; 15 - 80 nm |
| EIT: Extreme-Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope PI: J.-P. Delaboudiniere; Institute d'Astrophysique Spatiale, France |
Full disk imager; evolution of chromospheric and coronal structures |
| UVCS: Ultraviolet Coronograph Spectrometer PI: J.L. Kohl; Harvard CFA, USA |
Coronal diagnostic between 1.3 and 10 R_sun |
| LASCO: Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph PI: G.E. Brueckner; Hulburt Center for Space Research, NRL, USA |
Triple white-light coronagraph, 1.1 - 30 R_sun |
| SWAN: Solar Wind Anisotropies PI: J.L. Berteaux; Service d'Aéronomie, CNRS, France |
Scanning telescopes with hydrogen absorption cell for Ly-a light |
| CELIAS: Charge, ELement and Isotope Analysis System PI: D. Hovestadt; Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Germany |
Solar wind energy distribution and composition, 0.1 - 1000 keV/e |
| COSTEP: COmprehensive SuperThermal and Energetic Particle analyser PI: R. Müller-Mellin; Institut für Kernphysik, Uni Kiel, Germany |
Solar wind energy distribution of ions, 0.04 - 53 MeV/n |
| ERNE: Energetic and Relativistic Nuclei and Electron experiment PI: J. Torsti; Space Research Laboratory, Turku, Finland |
Solar wind energy distribution and isotopic composition, p-Ni: 1.4 - 540 MeV/n; electrons: 5-60 MeV |